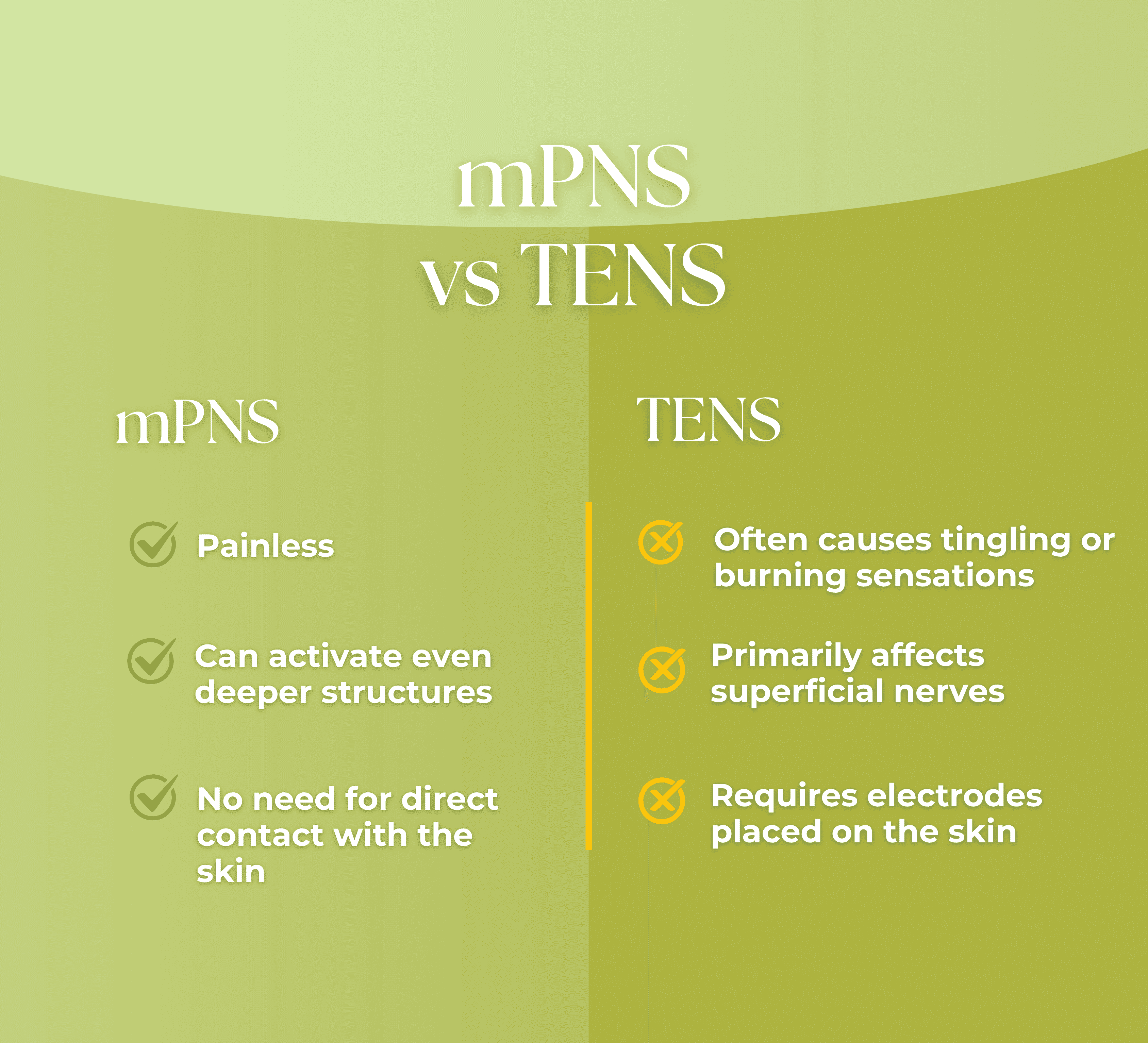
Significant Pain Reduction Shown in Clinical Trials
Studies such as Bedder & Parker (2023) and Leung et al. (2014) show that responding patients experienced significant pain relief, often after only a few sessions - with an average pain reduction of 87%. Importantly, the benefits frequently last for at least three months post-treatment, reducing the need for ongoing therapy and improving quality of life.
mPNS Therapy and Migraine
Leahu et al. (2020)
Scientific Reports, 10, 10572
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62701-9
** mPNS Therapy and Fibromyalgia**
Leenus et al. (2025)
Pain Management, 15(1), 45–53
https://doi.org/10.1080/17581869.2025.2459594
mPNS and Chronic Pain, Chronic Neuropathic Pain
Bedder & Parker (2023)
Journal of Pain Research, 16, 2365–2373
https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S409331
Dana et al. (2024)
Pain Practice, 24(1), 10-25
https://doi.org/10.1111/papr.13332
mPNS and Acute/Chronic Postsurgical Pain, (i.a. Axial pain after posterior cervical spine surgery)
Park et al. (2023)
The Journal of Pain, 24(7), 1151–1162
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2023.02.031
Significant Neural Recovery Shown in Clinical Trials
In addition to pain relief, studies show that mPNS contributes to neural recovery:
Limb paresis after stroke
Obayashi & Takahashi (2020)
NeuroRehabilitation, 46(4), 569–575
https://doi.org/10.3233/NRE-203103
Spasticity post spinal cord injury
Li et al. (2022)
Frontiers in Neurology, 13, 967949
https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2022.967949
Frozen shoulder syndrome
Kumar et al. (2021)
Cureus, 13(6), e15945
https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.15945
Orthopaedic rehabilitation post-fracture
Yin et al. (2015)
Pain Medicine, 16(5), 953–960
https://doi.org/10.1111/pme.12657
Results from Key Studies (SEAT and Painful Diabetic Neuropathy)
A multicentre, randomised controlled trial investigated the safety and effectiveness of the Axon Therapy, the mPNS in adults suffering from chronic neuropathic pain following trauma or surgery.
The study reported:
- **Pain relief **(≥ 50%): 71% of patients who received both mPNS and standard treatment reached significant pain relief, while only 13% of those who got standard treatment alone did.
- **Mean pain score reduction **(VAS): The mPNS group reported a 3.8-point drop in symptoms (over 50% improvement), while the Conventional Medical Management (CMM) group had only a small 0.7-point drop (about 10%).
- **Quality of life **(EQ‑5D‑3L): Improved notably in the mPNS + CMM group, with little to no change seen in the CMM‑only group
- Patient Global Impression of Change: 80.6% in the mPNS group rated their overall condition as improved, versus only 4.3% in the conventional treatment.
mPNS combined with standard medical therapy can be significantly more effective than standard therapy alone in managing chronic pain: post-traumatic and post-surgical neuropathic pain.
Fast Onset of Relief and Lasting Effects
A major advantage of mPNS therapy is its rapid onset of action - study from Bedder, M., & Parker, L. (2023) showed a rapid improvement starting from the first treatment. Effects often persist for at least 3 months, and in some cases, longer. This sustained relief leads to a significant improvement in quality of life and helps reduce reliance on other therapies.
 Fig. Graph showing the rapid improvement observed already after the first treatment in the study from Bedder, M., & Parker, L. (2023).
Fig. Graph showing the rapid improvement observed already after the first treatment in the study from Bedder, M., & Parker, L. (2023).
Potential to Reduce Reliance on Pain Medications
Scientific data confirm that mPNS can reduce the need for analgesics. In the study by Bedder & Parker (2023), 58.3% of patients who responded to treatment reduced their opioid intake, helping prevent tolerance and addiction.
Reference:
Bedder, M., & Parker, L. (2023). Journal of Pain Research, 16, 2365–2373 https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S409331

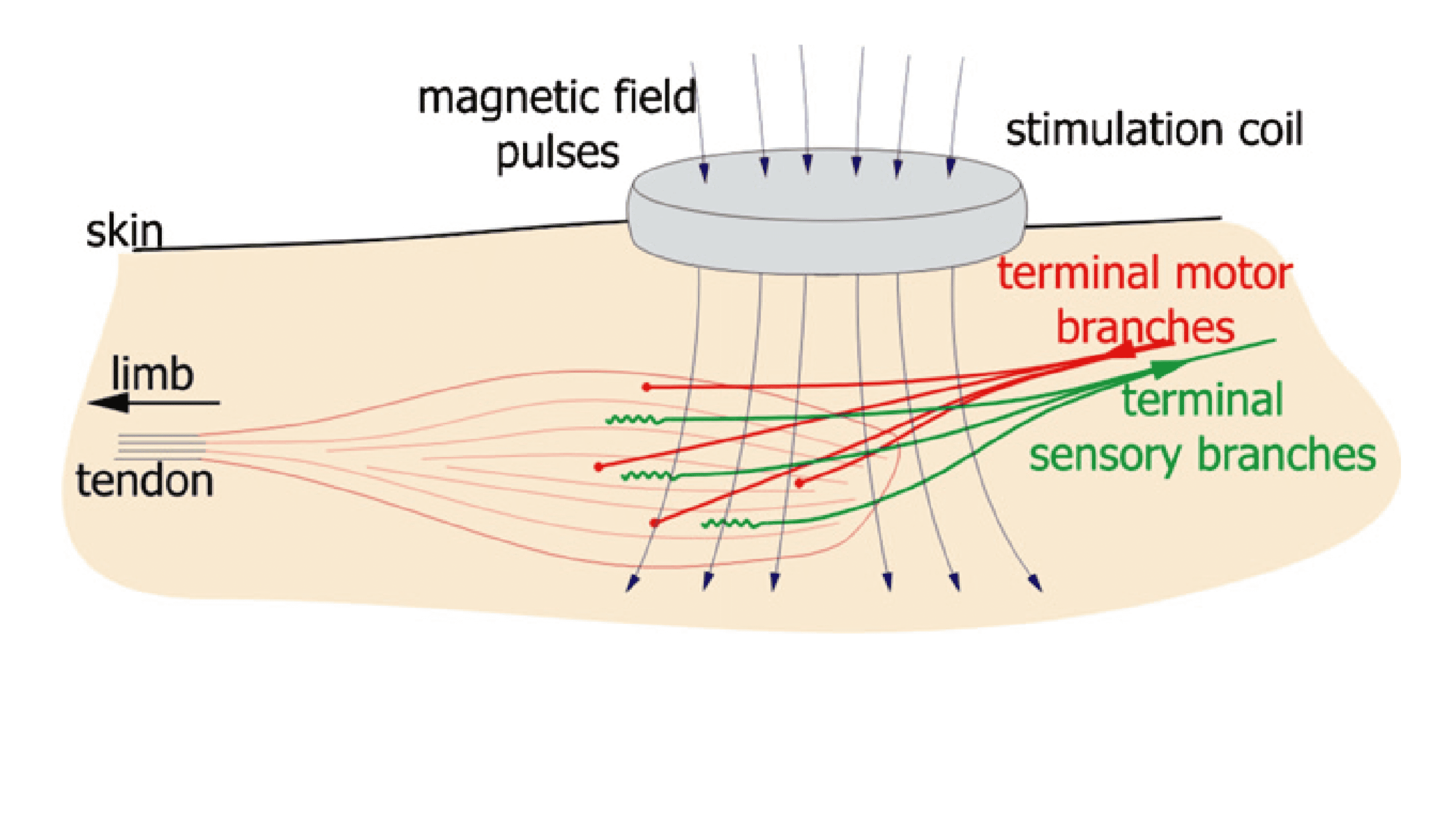

 Fig. Graph showing the rapid improvement observed already after the first treatment in the study from Bedder, M., & Parker, L. (2023).
Fig. Graph showing the rapid improvement observed already after the first treatment in the study from Bedder, M., & Parker, L. (2023).