Epilepsy diagnosis:
The diagnosis of epilepsy consists of several stages and procedures aimed at diagnosing epilepsy and confirming this neurological disorder.
Briefly, the diagnosis of epilepsy includes:
- Medical history and symptom analysis. The doctor conducts a detailed medical history, during which the patient describes his symptoms, frequency of seizures, duration, and characteristic features of their epileptic seizure. It is essential to gather information about triggers, family history of epilepsy, and other relevant medical conditions or medications the patient takes.
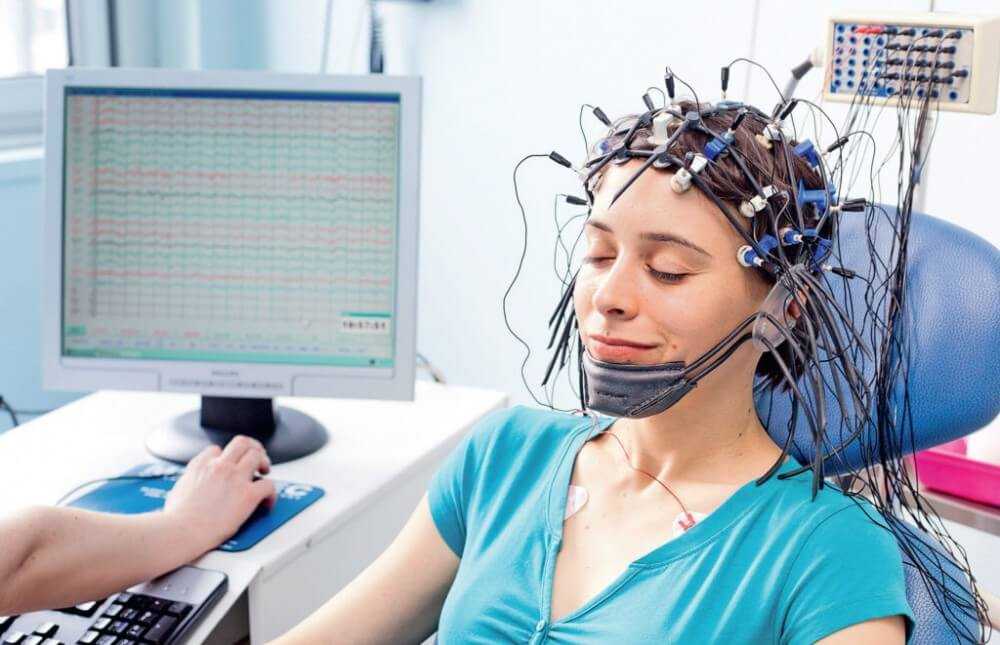
- Electroencephalography (EEG): This is one of the essential diagnostic tools for epilepsy. It involves placing electrodes on the patient's scalp to monitor the brain's electrical activity. EEG helps detect abnormal patterns of electrical activity that are characteristic of epilepsy.
- Brain imaging tests: Your doctor may recommend brain imaging tests, such as a computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan. These tests assess the brain's structure and rule out other possible causes of symptoms, such as brain tumors or injuries.